This guide represents the synergy of the latest technologies from Apple and Jamf. It harnesses the power of the new Declarative Device Management (DDM) framework built into macOS 15 (Sequoia). This modern approach is unlocked by Jamf Pro version 11.8.0 or later, which introduces Software Update Blueprints. Critically, this entire workflow is powered by the Jamf Account SSO, which connects your instance to the cloud micro-services required for Blueprints to function, creating a truly modern administrative experience.
The guide outlines the modern, three-part strategy for managing macOS 15 and newer in Jamf Pro. It leverages DDM via Blueprints for a reliable, automated workflow and is based on enterprise best practices for both aggressive and controlled rollouts.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure your environment meets these minimum requirements:
- Jamf Pro: Version 11.18.0 or later.
- Target Computers: macOS 15 (Sequoia) or later.
- Device Supervision: Devices must be Supervised.
- Administrator Authentication: Single Sign-On (SSO) must be enabled for your Jamf Pro user accounts to ensure a modern and secure administrative environment. For more information, see Jamf SSO.
- Apple Push Notification service (APNs): A valid APNs certificate is required for all communication.
A Primer on Declarative Device Management (DDM)
It is important to understand why this new method is superior to older approaches.
- The “Old Way” (MDM Commands & Scripts): Previously, managing updates was a “command and control” process where the Jamf Pro server sent direct push commands. This was often unreliable if devices were offline and required third-party tools and scripts to fill gaps in persistence and user experience.
- The “New Way” (DDM & Blueprints): Declarative Device Management is a “desired state” model. The server sends a declaration to the device describing the goal (e.g., “be on the latest macOS, after a 30-day delay”). The device itself becomes responsible for achieving this state autonomously, reporting its progress back. This is more resilient, reliable, and provides richer status reporting. Blueprints are Jamf’s tool for creating and deploying these declarations.
Part 1: The “All-in-One” Policy with Jamf Pro Blueprints
For macOS 15+, Blueprints are the definitive way to manage updates. This single object contains all the rules for your fleet, eliminating the need for multiple, complex profiles.
- In Jamf Pro, navigate to Blueprints. For more information, see the Jamf Pro Blueprints Configuration Guide.
- Click Create blueprint and name it [macOS 15+] Standard Update Policy.
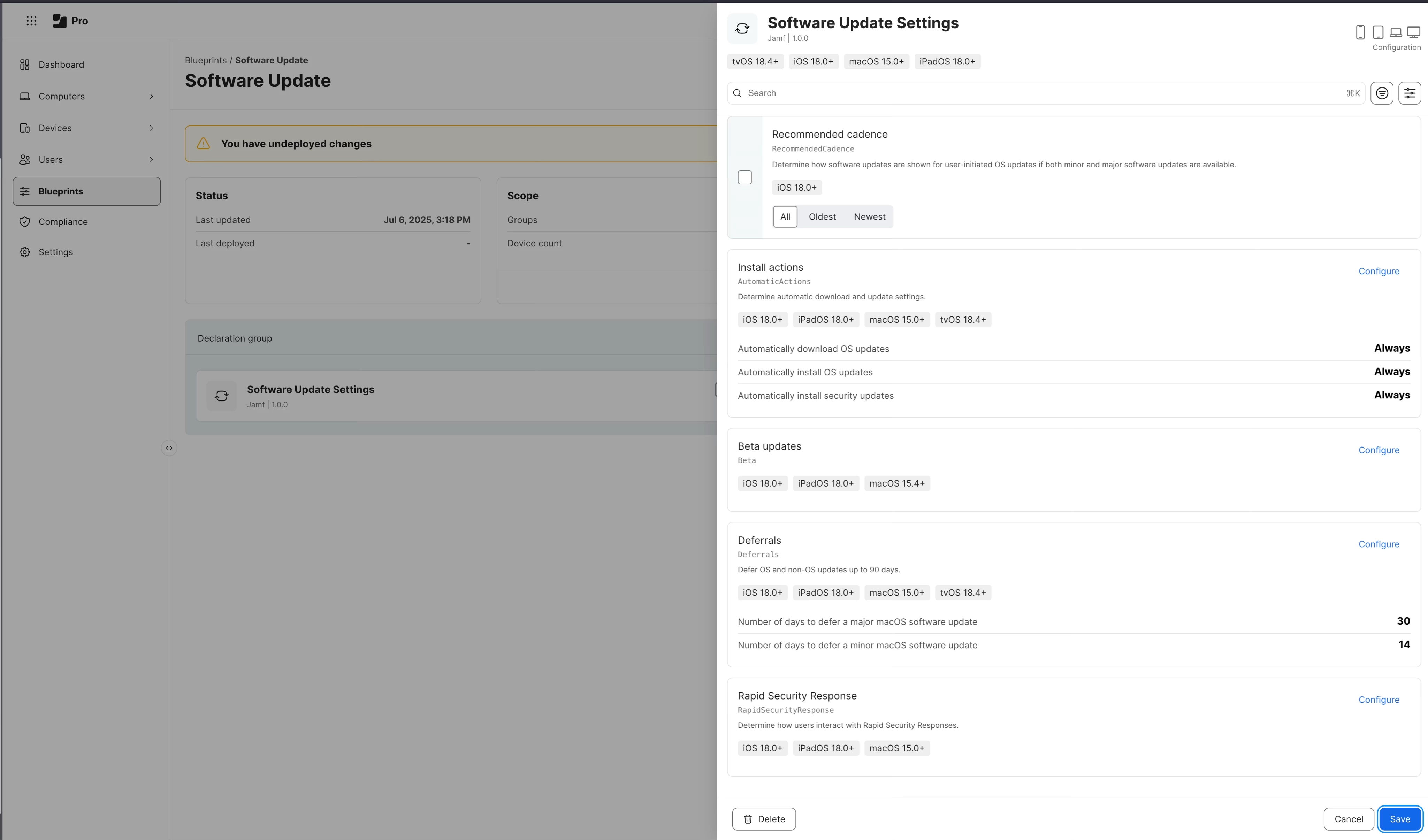
- Drag the Software Update Settings component into the builder and click Configure.
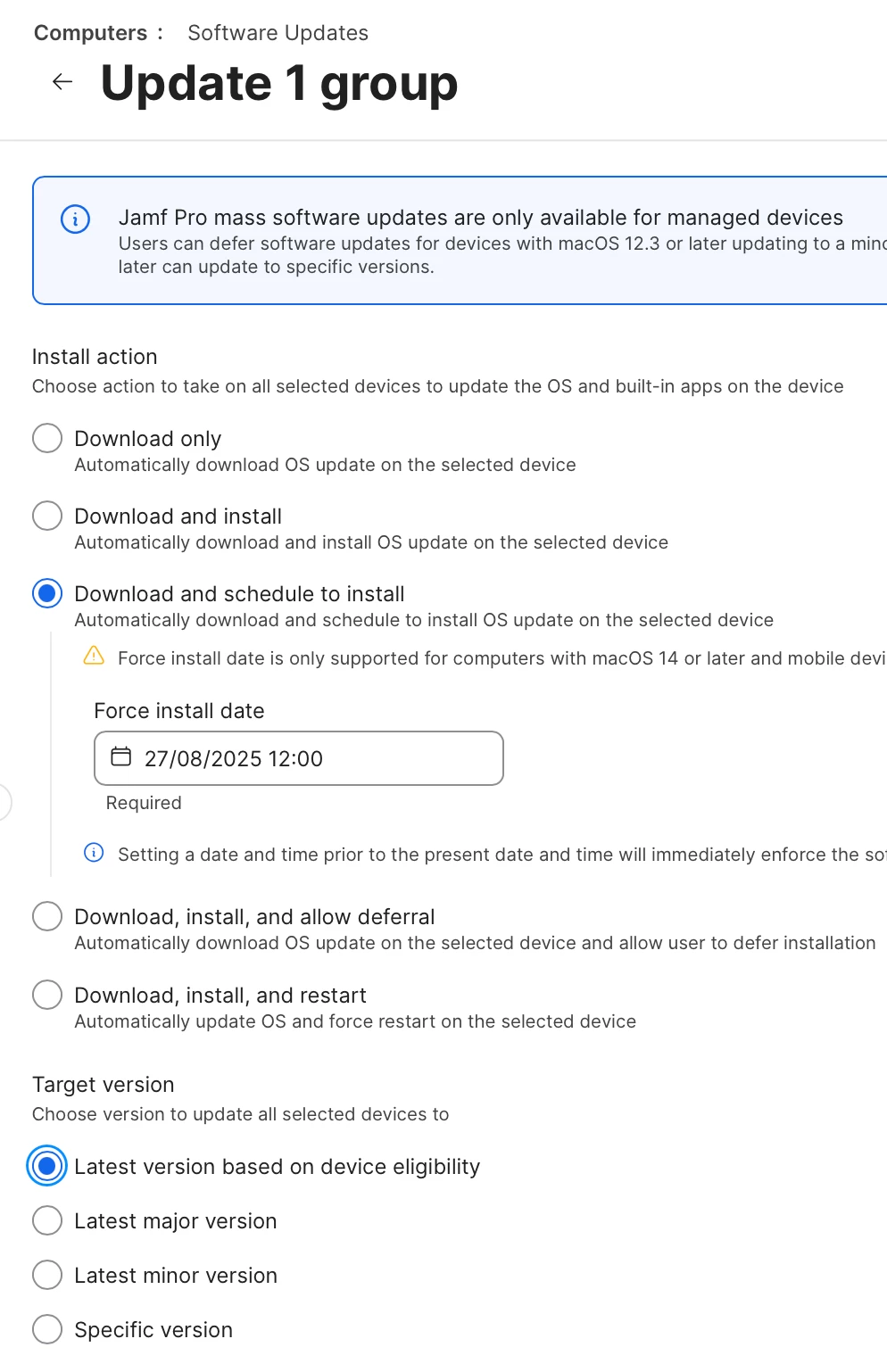
- Set Your Deferral Period: This is the first and most critical step, as it creates your testing window. Set your deferral days. A common enterprise policy is:
-
- Major OS Deferral Days: 30
- Minor OS Deferral Days: 14
5. Configure Automatic Install Actions: Next, tell devices how to act once the deferral period is over.
-
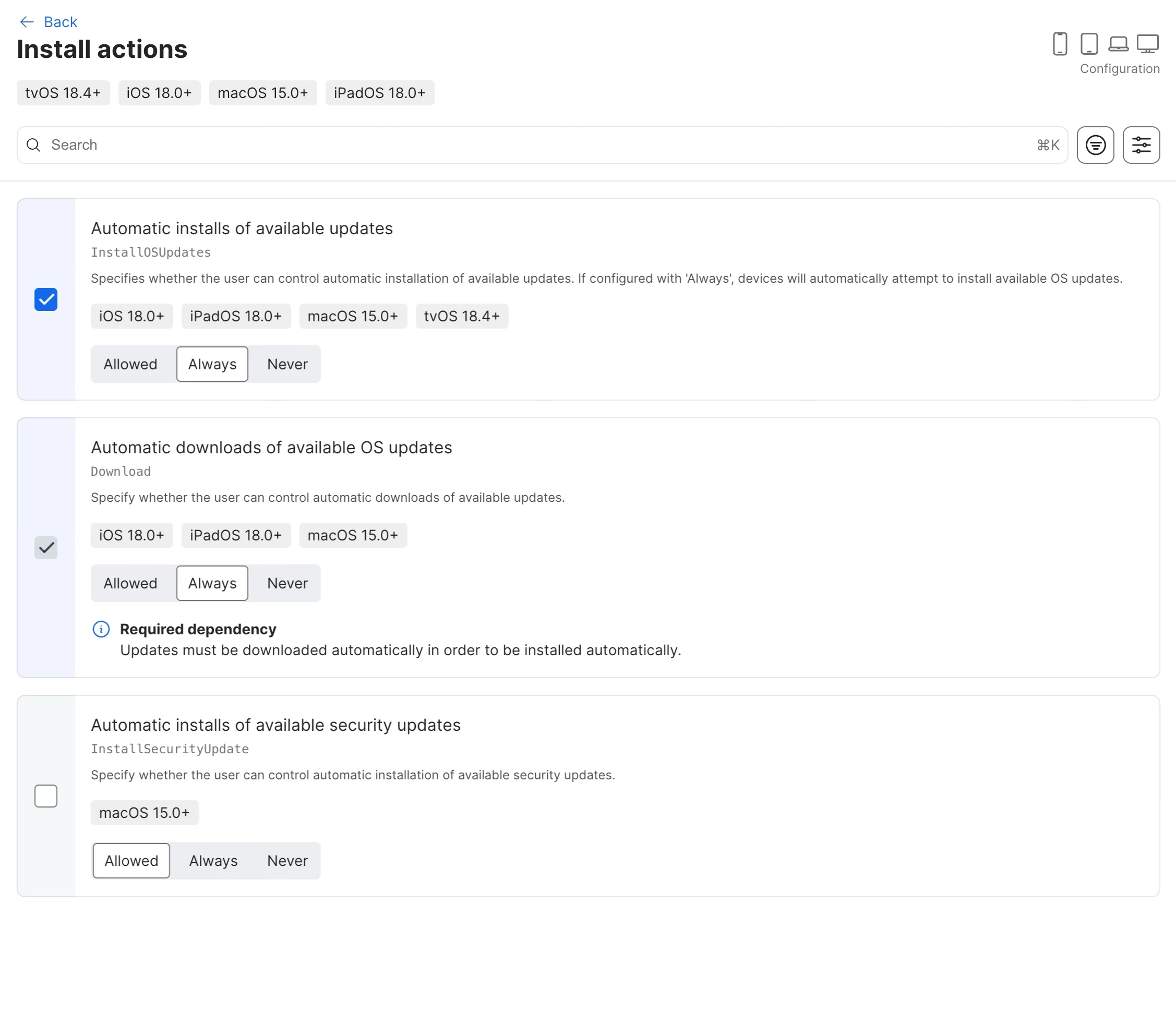
- Find the Install actions section and click its Configure button.
- For OS Updates: Under Automatic installs of available updates, check the box and select Always.
- For Security Updates: Under Automatic installs of available security updates, you must also check the box separately and select Always.
- Save the component and then Save the Blueprint.
- Scope the Blueprint to your macOS 15+ computer group and click Deploy.
Note: The “Software Update Settings” component contains additional options. For this core workflow, they are not essential and can be left at their default values.
Part 2: Monitoring and Reporting
Choose a monitoring strategy that matches your organization’s policy.
Step 2.1: Create the macOS Patch Software Title (Required for “Latest” Tracking)
This one-time setup enables robust reporting for the “latest version” strategy.
- Navigate to Computers > Patch Management. For more details, see Patch Management Software Titles.
- Click New, search for macOS, and select the relevant title (e.g., “Apple macOS Sequoia”).
- Save the title.
Step 2.2: Create a Compliance Smart Group
Option A: Tracking the Absolute Latest Version (Recommended)
- Display Name: [macOS 15+] Patch Compliance: Not on Latest OS.
- Criteria: Patch Reporting: Software Title > “Apple macOS Sequoia” | is not | Latest Version.
- Click Save.
Option B: Tracking a Specific, Approved Version (Alternative)
Use this when the latest version (e.g., 15.5) is deferred, and your goal is to enforce the previously approved version (15.4).
- Display Name: [macOS 15+] Compliance: Not on Approved Version (15.4).
- Criteria: Operating System Version | less than | 15.4.
- Click Save.
Part 3: Periodic Maintenance & Enforcement
This is your periodic task to enforce compliance. The enforcement action must match the Smart Group you are targeting.
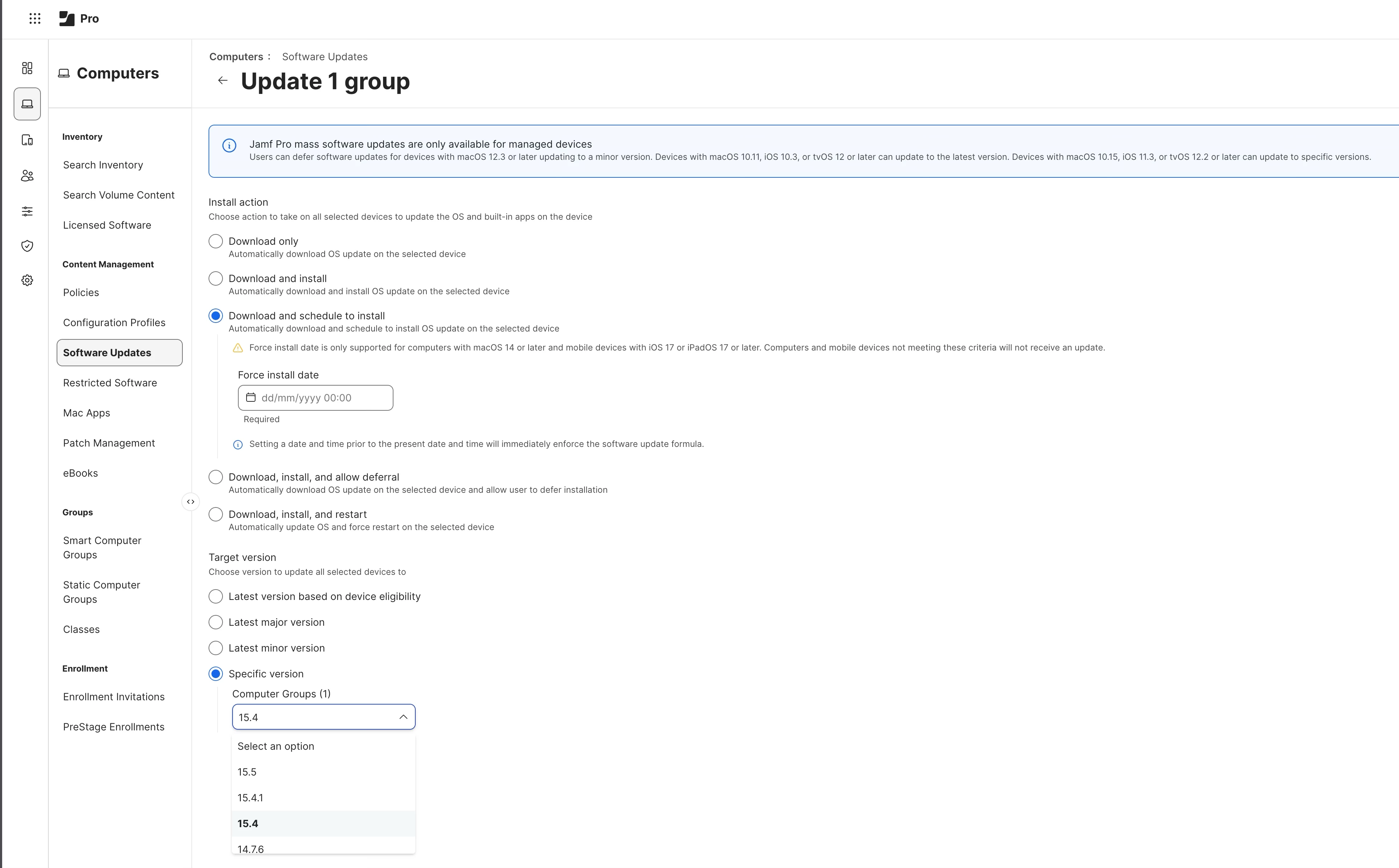
- Navigate to Computers > Software Updates. For details, see Managed Software Updates for macOS.
- Select the appropriate Smart Group from Part 2.
- Click Update Selected.
- Configure the DDM action that aligns with your goal:
Choice A: Enforcing the “Latest” Version
- Version: Keep the default: Latest version based on device eligibility.
- Schedule Type: Force install at date and time.
Choice B: Enforcing a “Specific” Version
- Version: Change to Specific version (e.g., 15.4).
- Schedule Type: Force install at date and time.
After configuring, click Apply to send the enforcement command.
Appendix: Troubleshooting Common Issues
Troubleshooting Blueprints & DDM (Part 1)
Monitoring and troubleshooting the status of DDM declarations is an advanced topic that currently relies on using the Jamf Pro API, not a graphical interface within a computer’s record.
For detailed, technical instructions, refer to the official Jamf documentation:
- Official Guide: Jamf Pro Blueprints Management
This guide provides the necessary API endpoints for administrators to programmatically check the status of deployed Blueprints.
Troubleshooting Managed Software Updates (Part 3)
When a manual enforcement command fails, you can use the GUI to investigate the target computer’s record.
1. Check the Command Status:
- Go to the Management tab -> Pending Commands and Completed Commands.
- If a command is stuck in “Pending,” the device may be offline or have APNs issues. See Troubleshooting APNs.
- Check Failed Commands for specific error messages.
2. Check for Common Prerequisites:
- Supervision: The device must be Supervised.
- Bootstrap Token (Critical for Apple silicon): For an update to install without user password entry, Jamf Pro must hold a Bootstrap Token. Check its status in the computer’s inventory under Security. For more information, see Leveraging Apple’s Bootstrap Token.
- Disk Space & Power: The device must have sufficient free storage and be connected to power or adequately charged.